GreenDao
简述
当我们编写好了Entity类之后,会自动生成DaoMaster、DaoSession、Entity Dao这三个核心类。
//生成数据库文件,名为students-db
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper helper = new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this, "xxx.db", null);
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
//建立特定模式下的所有的DAO对象和数据库db对象的映射
DaoMaster master = new DaoMaster(db);
//管理特定模式下的所有DAO对象,并提供一些通用的CRUD持久化方法
DaoSession session = master.newSession();
//得到指定的EntityDao对象
EntityDao dao = session.getEntityDao();
UML图
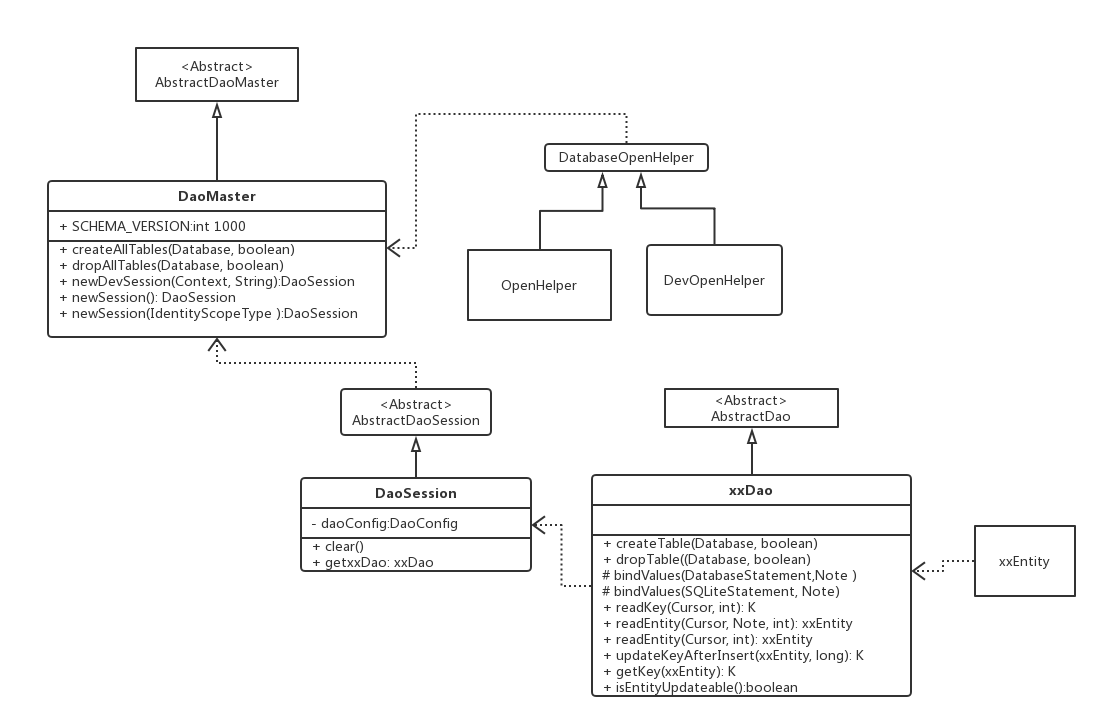
1. DaoMaster
public static void createAllTables(Database db, boolean ifNotExists) {
UserDao.createTable(db, ifNotExists);
}
public static void dropAllTables(Database db, boolean ifExists) {
UserDao.dropTable(db, ifExists);
}
public static class DevOpenHelper extends OpenHelper {
public DevOpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory) {
super(context, name, factory);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
Log.i("greenDAO", "Upgrading schema from version " + oldVersion + " to " + newVersion + " by dropping all tables");
dropAllTables(db, true);
onCreate(db);
}
}
DaoMaster是GreenDao的入口类,其实在DaoMaster的内部它是负责一些数据库管理的工作比如对表的创建以及删除,而DevOpernHelper这个静态内部类则是用来创建数据库,获取可读写的数据库。
2. AbstractDaoMaster
protected final Map<Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>>, DaoConfig> daoConfigMap;
protected void registerDaoClass(Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>> daoClass) {
DaoConfig daoConfig = new DaoConfig(db, daoClass);
daoConfigMap.put(daoClass, daoConfig);
}
public abstract AbstractDaoSession newSession();
public abstract AbstractDaoSession newSession(IdentityScopeType type);
AbstractDaoMaster是DaoMaster的父类,它的内部除了持有数据库的版本以及数据库操作的接口外还持有一个daoConfigMap,用于存储了EntityDao与db数据库之前的映射关系。
3. AbstractDaoSession
AbstractDaoSession中会创建AbstractDao,然后提供简单的操作表的接口
private final Map<Class<?>, AbstractDao<?, ?>> entityToDao;
private volatile RxTransaction rxTxPlain;
private volatile RxTransaction rxTxIo;
这是AbstractDaoSession类中的三个成员,entityToDao主要是用于存储实体类与对应AbstractDao之间的映射关系,而各种对表的操作其实都是通过这个映射关系找到对应的AbstractDao然后操作,而RxTransaction是把当前的AbstractDaoSession做Rx化,主要用于异步数据库操作,把数据库的操作放到一个线程里面就可以实现从外部传入对数据库的操作。
4. AbstractDao
AbstractDao封装了和数据库进行的增删改查功能,除了基本的crud还有Tx结尾的带事务的crud以及Rx化的crud,除此之外还有其它的一些优化的措施:
public DatabaseStatement getInsertStatement() {
if (insertStatement == null) {
String sql = SqlUtils.createSqlInsert("INSERT INTO ", tablename, allColumns);
DatabaseStatement newInsertStatement = db.compileStatement(sql);
synchronized (this) {
if (insertStatement == null) {
insertStatement = newInsertStatement;
}
}
if (insertStatement != newInsertStatement) {
newInsertStatement.close();
}
}
return insertStatement;
}
Greendao中的数据库的操作都是使用Statement来进行优化性能的,而且Statement是可以重用的,GreenDao有它自己的Statement管理类,就是TableStatements。对于不同的数据库操作,TableStatements就持有不同的DatabaseStatement对象,比如上面的插入操作,TableStatements维护着一个insertStatement对象,如果不为null就直接返回,为null就拼接创建,以达到复用优化性能的作用,这是数据库常见的操作,而SqlUtils工具类是Sql语句拼接的工具。
以下是单体操作的源码(取插入为例)
private long executeInsert(T entity, DatabaseStatement stmt, boolean setKeyAndAttach) {
long rowId;
//先判断当前线程是否连接了数据库
if (db.isDbLockedByCurrentThread()) {
//返回true 直接插入数据
rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);
} else {
//在锁定stmt之前通过开启transation请求连接
db.beginTransaction();
try {
rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
} finally {
db.endTransaction();
}
}
if (setKeyAndAttach) {
updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(entity, rowId, true);
}
return rowId;
}
上面的代码操作步骤如下:
- 通过判断当前线程是否和数据库关联来决定是否需要开启事务。
- 最后都执行insertInsideTx,里面的操作就是调用子类的bindValue方法进行绑定值后执行SQL操作。
- 插入后的善后处理,这里就是更新实体的ID为RowId和做内存缓存,还有一些特殊操作实体绑定DaoSeesion,使用active = true会用到。
以下是多数据插入操作的源码(取插入为例)
private void executeInsertInTx(DatabaseStatement stmt, Iterable<T> entities, boolean setPrimaryKey) {
db.beginTransaction();
try {
synchronized (stmt) {
if (identityScope != null) {
identityScope.lock();
}
try {
if (isStandardSQLite) {
SQLiteStatement rawStmt = (SQLiteStatement) stmt.getRawStatement();
for (T entity : entities) {
bindValues(rawStmt, entity);
if (setPrimaryKey) {
long rowId = rawStmt.executeInsert();
updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(entity, rowId, false);
} else {
rawStmt.execute();
}
}
} else {
for (T entity : entities) {
bindValues(stmt, entity);
if (setPrimaryKey) {
long rowId = stmt.executeInsert();
updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(entity, rowId, false);
} else {
stmt.execute();
}
}
}
} finally {
if (identityScope != null) {
identityScope.unlock();
}
}
}
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
} finally {
db.endTransaction();
}
}
Statement的获取和上面的单体操作类似,而因为是多数插入,所以强制使用事务,而IdentityScope<K, T>是GreenDao用来做内存缓存的,可以看成是一个Map,如果是Long,GreenDao做了对应的优化,因为多数据插入是比较耗时的,所以,我们执行插入之前需要加锁,防止多线程的问题,但是多数插入其实也只是遍历插入而已 。
总结一下GreenDao的优化和缓存
- 通过Statement的复用,达到优化的效果,这是所有数据库都通用的。
- 通过Key映射保存到内存中(PS:保存的值为弱引用)。
- 在Key为Long时还特别做了Map的优化。(PS:Integer的HashCode就是自己,而Long则要把高32位异或下来变成int)
参考资料:
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/50328930f6fb
- https://blog.csdn.net/u010782846/article/details/80295873
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35320040